Freezing Point Of Ethyl Alcohol
Ethanol (Ethyl Alcohol), C2H5OH, is a volatile,flammable, colorless liquid with a slight feature odor. It is produced via petrochemical processes or naturally by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts.
Ethanol is nigh commonly consumed as a popularrecreational drug. It is a psychoactive substance and is the principal type of booze found in alcoholic drinks. It besides has medical applications every bit an clarified and disinfectant. The compound is widely used as a chemical solvent, either for scientific chemical testing or in synthesis of other organic compounds. Ethanol is likewise used as a make clean-burning fuel source.
The phase diagram of ethanol is shown beneath the table.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethanol:
Values are given for liquid at 25oC /77oF / 298 Yard and 1 bara, if not other phase, temperature or pressure given.
For full tabular array with Purple Units - rotate the screen!
| Belongings | Value | Unit of measurement | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | |||
| Acidity (pKa1) | 15.ix | ||||||||||
| Autoignition temperature | 636 | K | 363 | °C | 685 | °F | |||||
| Boiling Indicate | 351.39 | K | 78.2 | °C | 172.8 | °F | |||||
| Critical density | 5.91 | mol/dmiii | 272 | kg/m3 | 0.528 | slug/ft3 | 17.0 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Disquisitional Force per unit area | 6.25 | MPa=MN/m2 | 62.five | bara | 61.7 | atm | 906 | psia=lbf/intwo | |||
| Critical temperature | 513.9 | K | 240.viii | °C | 465.4 | °F | |||||
| Critical Volume | 169 | cm3/mol | 0.00367 | one thousand3/kg | 1.89 | ftiii/slug | 0.0588 | ft3/lb | |||
| Density (gas) at 0.08 bar | iii.15 | mol/m3 | 0.145 | kg/m3 | 0.00028 | slug/ftthree | 0.0091 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Density (liquid) | 17046 | mol/miii | 785.3 | kg/giii | 1.524 | slug/ftiii | 49.02 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Flammable (gas and liquid) | yes | ||||||||||
| Wink signal | 286 | 1000 | 13 | °C | 55 | °F | |||||
| Gas abiding (individual) - R | 180.5 | J/kg K | 0.05013 | Wh/(kg Yard) | 1079 | [ft lbf/slug °R] | 33.54 | [ft lbf/lb °R] | |||
| Gibbs complimentary free energy of formation (gas) | -168 | kJ/mol | -3647 | kJ/kg | -1568 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Specific oestrus capacity, Cp (isobaric) (gas) | 74 | J/mol Chiliad | 1.60 | kJ/kg G | 0.383 | Btu/lb°F or cal/1000 M | |||||
| Specific heat capacity, Cp (liquid) | 118 | J/mol One thousand | 2.57 | kJ/kg Yard | 0.614 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g Yard | |||||
| Specific heat capacity, Cv (isochoric) (gas) | 65 | J/mol K | 1.42 | kJ/kg G | 0.339 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Specific rut capacity, Cv (liquid) | 100 | J/mol K | ii.18 | kJ/kg One thousand | 0.520 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of combustion (gas) | 1336.eight | kJ/mol | 29017 | kJ/kg | 12.5 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of formation (gas) | -234 | kJ/mol | -5079 | kJ/kg | -2184 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of fusion at -173°F/-114°C | four.9 | kJ/mol | 106 | kJ/kg | 45.73 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of evaporation | 42.32 | kJ/mol | 919 | kJ/kg | 394.94 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Ionization potential | 10.47 | eV | |||||||||
| log KOW (Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient) | -0.31 | ||||||||||
| Melting point | 159.01 | Thou | -114.1 | °C | -173.5 | °F | |||||
| Molecular Weight | 46.069 | g/mol | 0.10156 | lb/mol | |||||||
| Solubility in h2o | 1000 | mg/ml | |||||||||
| Sound velocity in liquid | 1139 | m/south | 3736 | ft/due south | 2551 | mi/h | |||||
| Sound velocity in gas, at 0.08 bara | 246 | yard/s | 807 | ft/s | 551 | mi/h | |||||
| Specific Gravity (gas) (relativ to air) | 1.59 | ||||||||||
| Specific Gravity (liquid) (relativ to water) | 0.79 | ||||||||||
| Specific Estrus Ratio (gas) - Cp/Cv | 1.13 | ||||||||||
| Specific Estrus Ratio (liquid) - Cp/Cv | 1.18 | ||||||||||
| Specific Volume (gas), at 0.08 bar | 0.318 | chiliad3/mol | 6.90 | thou3/kg | 3554 | ft3/slug | 110 | ft3/lb | |||
| Specific Volume, (liquid) | 0.0000587 | m3/mol | 0.00127 | g3/kg | 0.656 | ft3/slug | 0.0204 | ftthree/lb | |||
| Standard molar entropy, South° (gas) | 283 | J/mol K | vi.14 | kJ/kg Chiliad | 1.47 | Btu/lb °F | |||||
| Standard molar entropy, S° (liquid) | 160 | J/mol One thousand | 3.47 | kJ/kg K | 0.83 | Btu/lb °F | |||||
| Surface tension | 21.97 | dynes/cm | 0.02197 | Due north/m | |||||||
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.167 | Due west/m 1000 | 0.0965 | Btu/hour ft °F | |||||||
| Triple point pressure | four.3x10-x | MPa=MN/thousand2 | iv.3x10-9 | bara | 4.24x10-9 | atm | 6.24x10-8 | psia=lbf/in2 | |||
| Triple bespeak temperature | 150.00 | K | -123.15 | °C | -189.67 | °F | |||||
| Vapor (saturation) force per unit area | 0.008 | MPa=MN/mii | 60.0 | mm Hg | 0.0790 | atm | one.16 | psi=lbf/intwo | |||
| Viscosity, dynamic (accented) | i.074 | cP | 721.7 | [lbk /ft due south*x-6] | 22.43 | [lbf south/fttwo *10-vi] | |||||
| Viscosity, kinematic | ane.36 | cSt | fourteen.six | [ft2/south*10-6] |
Dorsum to top
Follow the links below to get values for the listed backdrop of ethanol at varying pressure and temperature:
- Density and specific weight
- Dynamic and kinematic viscosity
- Specific Heat (Heat Capacity), Cp and Cfive
See also more near atmospheric pressure, and STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure & NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure,
besides as Thermophysical properties of: Acetone, Acetylene, Air, Ammonia, Argon, Benzene, Butane, Carbon dioxide, Carbon monoxide, Ethane, Ethylene, Helium, Hydrogen, Hydrogen sulfide, Methyl hydride, Methanol, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Pentane, Propane, Toluene, H2o and Heavy water, DtwoO.
Ethanol is a liquid at standard atmospheric condition. However, at depression temperature and/or very high pressures it becomes a solid.
The phase diagram for ethanol shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The bend between the disquisitional point and the triple point shows the ethanol humid betoken with changes in pressure. Information technology as well shows the saturation force per unit area with changes in temperature.
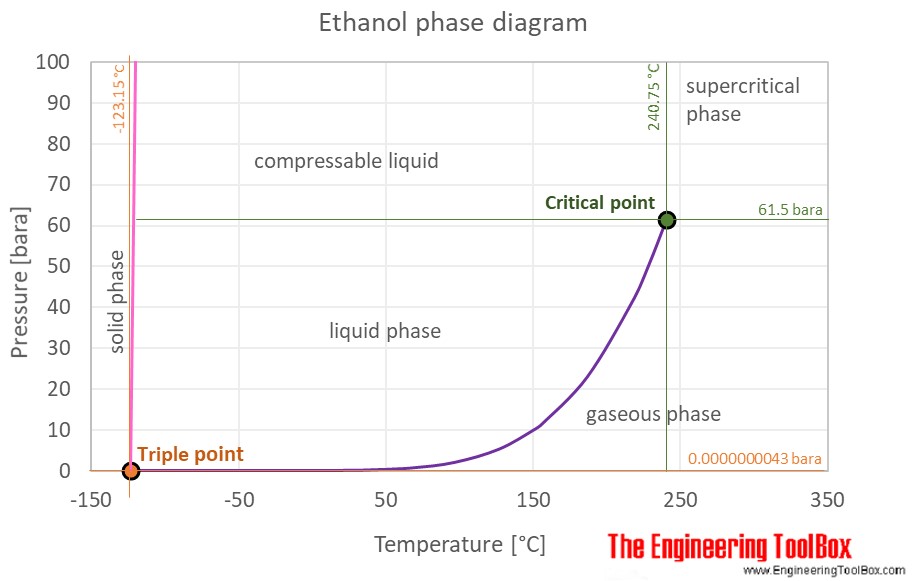
At the critical betoken there is no alter of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added.
The triple signal of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the iii phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Back to top
Freezing Point Of Ethyl Alcohol,
Source: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/ethanol-ethyl-alcohol-properties-C2H6O-d_2027.html
Posted by: muirtragivan.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Freezing Point Of Ethyl Alcohol"
Post a Comment