As Element Metal Or Nonmetal
Metals
In the periodic table, you tin see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron (B), atomic number 5, and going all the manner down to Polonium (Po), diminutive number 84. Except for Germanium (Ge) and Antimony (Sb), all the elements to the left of that line can be classified as metals.These metals have properties that you normally associate with the metals you come across in everyday life:
-
They are solid (with the exception of mercury, Hg, a liquid).
-
They are shiny, adept conductors of electricity and rut.
-
They are d uctile (they tin can exist drawn into thin wires).
-
They are malleable (they tin can exist easily hammered into very thin sheets).
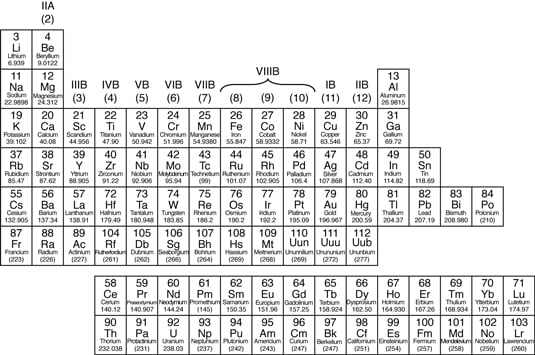
The metals in the periodic table.
Nonmetals
Except for the elements that edge the stair-stepped line, the elements to the right of the line are classified as nonmetals (along with hydrogen). Nonmetals have properties contrary those of the metals.The nonmetals are brittle, not malleable or ductile, poor conductors of both heat and electricity, and tend to gain electrons in chemic reactions. Some nonmetals are liquids. These elements are shown in the following figure.
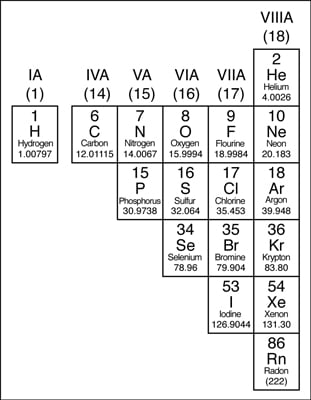
The nonmetals in the periodic table.
Metalloids
The elements that edge the stair-stepped line are classified as metalloids. The metalloids, or semimetals, accept properties that are somewhat of a cross between metals and nonmetals.Metalloids tend to be economically important because of their unique conductivity properties (they only partially conduct electricity), which make them valuable in the semiconductor and computer chip manufacture. The metalloids are shown in the post-obit illustration.
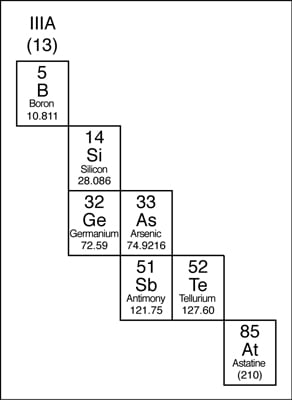
The metalloids in the periodic table.
Nearly This Article
This article can exist plant in the category:
- Chemistry ,
As Element Metal Or Nonmetal,
Source: https://www.dummies.com/article/academics-the-arts/science/chemistry/the-periodic-table-metals-nonmetals-and-metalloids-194223/
Posted by: muirtragivan.blogspot.com


0 Response to "As Element Metal Or Nonmetal"
Post a Comment